Linux网络I/O模型简介
根据UNIX网络编程对I/O模型的分类,unix提供了5种I/O模型:
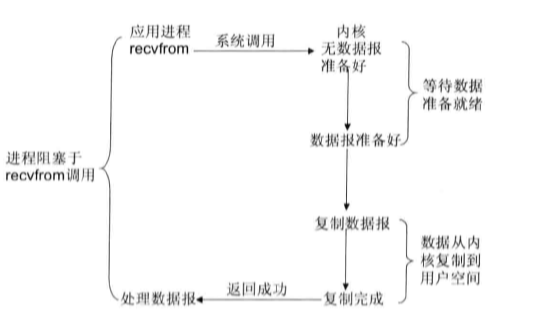
- 阻塞I/O模型:最常用的I/O模型就是阻塞I/O模型,缺省情况下,所有文件操作都是阻塞的。以套接字接口为例来讲解此模型:在进程空间中调用recvfrom,其系统调用会直到数据包到达且被复制到应用进程的缓冲区中或者发生错误时才返回,在此期间一直会等待,进程在从调用recvfrom开始到它返回的整段时间内都是被阻塞的。
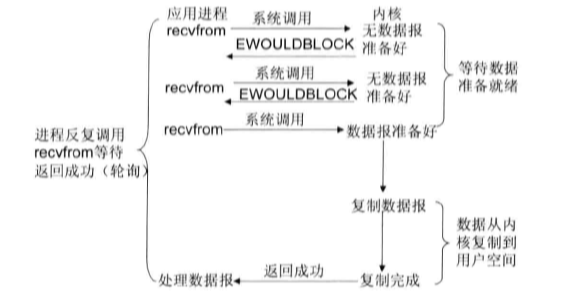
- 非阻塞I/O模型:recvfrom从应用层到内核的时候,如果该缓冲区没有数据的话,就直接返回一个EWOULDBLOCK错误,一般对非阻塞I/O模型进行轮询检查这个状态,看内核是不是有数据到来
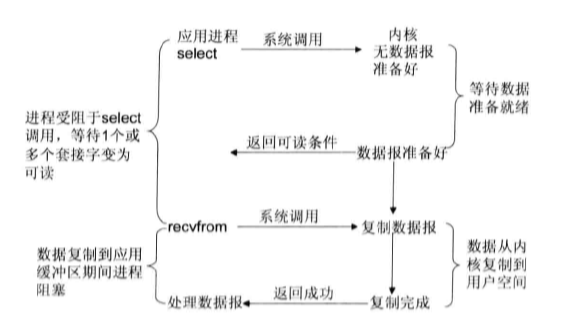
- I/O复用模型:Linux提供select/poll,进程通过一个或多个fd(文件描述符)传递给select或poll系统调用,阻塞在select操作上,这样select/poll可以帮我们侦测多个fd是否处于就绪状态。select/poll是顺序扫描fd是否就绪,而且支持的fd数量有限,因此它的使用受到了一些制约。Linux还提供了一个epoll系统调用,epoll使用基于事件驱动方式代替顺序扫描,因此性能更高
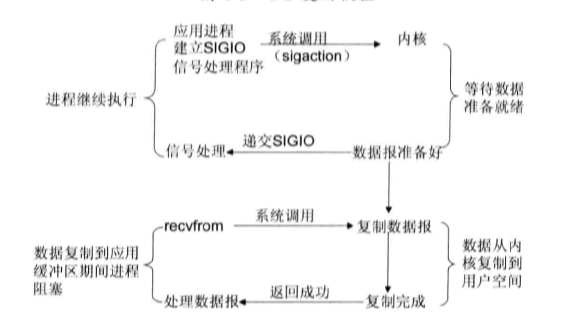
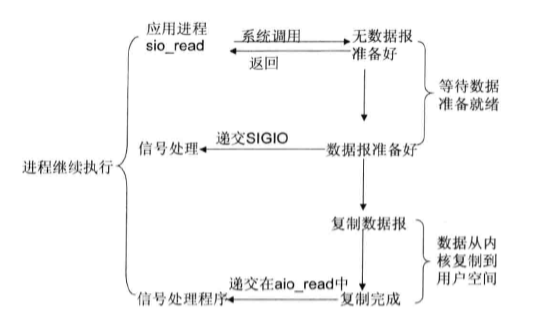
- 信号驱动I/O模型:首先开启套接口信号驱动I/O功能,并铜鼓哦系统调用sigaction执行一个信号处理函数(此系统调用立即返回,进程继续工作,它是非阻塞的)。当数据准备就绪时,就为该进程生成一个SIGIO信号,通过信号回调通知应用程序调用recvfrom来读取数据,并通知主循环函数处理数据
- 异步I/O:告知内核启动某个操作,并让内核在整个操作完成后(包括将数据从内核复制到用户自己的缓冲区)通知我们。这种模型与信号驱动模型的主要区别是:信号驱动I/O由内核通知我们核是可以开始一个I/O操作;异步I/O模型由内核通知我们I/O操作何时已经完成
Java中BIO存在的问题
每当有一个新的客户端请求接入时,服务端必须创建一个新的线程处理新介入的客户端链路,一个线程只能处理一个客户端连接。在高性能服务器应用领域,往往需要面向成千上万个客户端的并发连接,这种模型显然无法满足高性能、高并发接入的场景。为了改进一线程一连接模型,后来又演进除了一种通过线程池或者消息队列实现1或者多个线程处理N个客户端的模型,由于它的底层通信机制依然使用同步阻塞I/O,所以被称为“伪异步”。Java中NIO概念
- 缓冲区Buffer:在NIO库中,所有数据都是用缓冲区处理的。在读取数据时,它是直接读到缓冲区中的。在写入数据时,写入到缓冲区中。任何时候访问NIO的数据,都是通过缓冲区进行操作。缓冲区实质上是一个数组,通常是一个字节数组,也可以是使用其他种类的数组,它又不仅仅是一个数组,缓冲区提供了对数据的结构化访问以及维护读写位置等信息。
- 通道Channel:Channel时一个通道,网络数据通过Channel读取和写入,它与流的不同之处在于通道是双向的,流只是在一个方向上移动(一个流必须是InputStream或者OutputStream的子类),而通过可以用于读、写或者二者同时进行。
- 多路复用器Selector:Selector对于NIO编程至关重要,多路复用器提供选择已经就绪的任务的能力,Selector会不断轮询注册在其上的Channel,如果某个Channel上面发生读或者写时间,这个Channel就出于就绪状态,会被Selector轮询出来,然后通过SelectionKey可以获取就绪Channel的集合。一个多路复用器Selector可以同时轮询多个Channel,由于JDK使用了epoll()代替传统的select实现,所以它并没有最大连接句柄1024/2018的限制,也就意味着只需要一个线程负责Selector的轮询,就可以接入成千上万的客户端。

NIO优势
- 客户端发起的连接操作是异步的,可以通过在多路复用器注册OP_CONNECT等到后续结果,不需要像之前的客户端那样被同步阻塞
- SocketChannel的读写操作都是异步的,如果没有可读写的数据它不会同步等待,直接返回,这样I/O通信线程就可以处理其他的链路,不需要同步等到这个链路可用
- 线程模型的优化:由于JDK的Selector在Linux等主流操作系统上通过epoll实现,它没有连接句柄数的限制(只限制于操作系统的最大句柄数或者对单个进程的句柄限制),这意味着一个Selector线程可以同时处理N个客户端连接,而且性能不会随着客户端的增加而线性下降,因此非常适合做高性能、高负载的网络服务器。
netty的一个demo
client
EchoClient
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
| public class EchoClient {
private String host;
private Integer port;
private NioEventLoopGroup nioEventLoopGroup = null;
public EchoClient(String host, Integer port){
this.host = host;
this.port = port;
}
public void start() throws Exception{
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
nioEventLoopGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
bootstrap.group(nioEventLoopGroup)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.remoteAddress(new InetSocketAddress(host, port))
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new EchoClientHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect().sync();
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}finally {
nioEventLoopGroup.shutdownGracefully().sync();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
EchoClient echoClient = new EchoClient("localhost", 20000);
echoClient.start();
}
}
|
EchoClientHandler
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| public class EchoClientHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<ByteBuf> {
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println("客户端连接服务器, 开始发送数据......");
byte[] req = "QUERY TIME ORDER".getBytes();
ByteBuf firstMessage = Unpooled.buffer(req.length);
firstMessage.writeBytes(req);
ctx.writeAndFlush(firstMessage);
}
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, ByteBuf msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println("client 读取server数据......");
byte[] resp = new byte[msg.readableBytes()];
msg.readBytes(resp);
String body = new String(resp, "UTF-8");
System.out.println("服务端数据为: " + body);
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
System.out.println("client exceptioncaught");
ctx.close();
}
}
|
server
EchoServer
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
| public class EchoServer {
private final Integer port;
public EchoServer(Integer port){
this.port = port;
}
public void start() throws Exception{
EventLoopGroup eventExecutors = null;
try {
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
eventExecutors = new NioEventLoopGroup();
serverBootstrap.group(eventExecutors)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.localAddress("localhost", port)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<Channel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel channel) throws Exception {
channel.pipeline().addLast(new EchoServerHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind().sync();
System.out.println("开始监听, 端口: " + channelFuture.channel());
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}finally {
if(eventExecutors != null){
eventExecutors.shutdownGracefully().sync();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
EchoServer echoServer = new EchoServer(20000);
echoServer.start();
}
}
|
EchoServerHandler
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| public class EchoServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
System.out.println("server 读取数据");
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf)msg;
byte[] req = new byte[buf.readableBytes()];
buf.readBytes(req);
String body = new String(req, "UTF-8");
System.out.println("接收client数据: " + body);
System.out.println("server向client发送数据");
String currentTime = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()).toString();
ByteBuf resp = Unpooled.copiedBuffer(currentTime.getBytes());
ctx.write(resp);
}
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
System.out.println("server 读取数据完毕");
ctx.flush();
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
System.out.println("server exceptionCaught");
ctx.close();
}
}
|
netty总结
- ChannelInboundHandler之间的传递,需通过调用ctx.fireChannelRead(msg)实现,调用ctx.write(msg)将传递到ChannelOutboundHandler
- ctx.write()方法执行后,需要调用flush()方法只能令它立即执行
- ChannelOutboundHandler在pipeline注册的时候需要放在最后一个ChannelInboundHandler之前,否则将无法传递到ChannelOutboundHandler。
- Handler的消费处理放在最后一个处理






